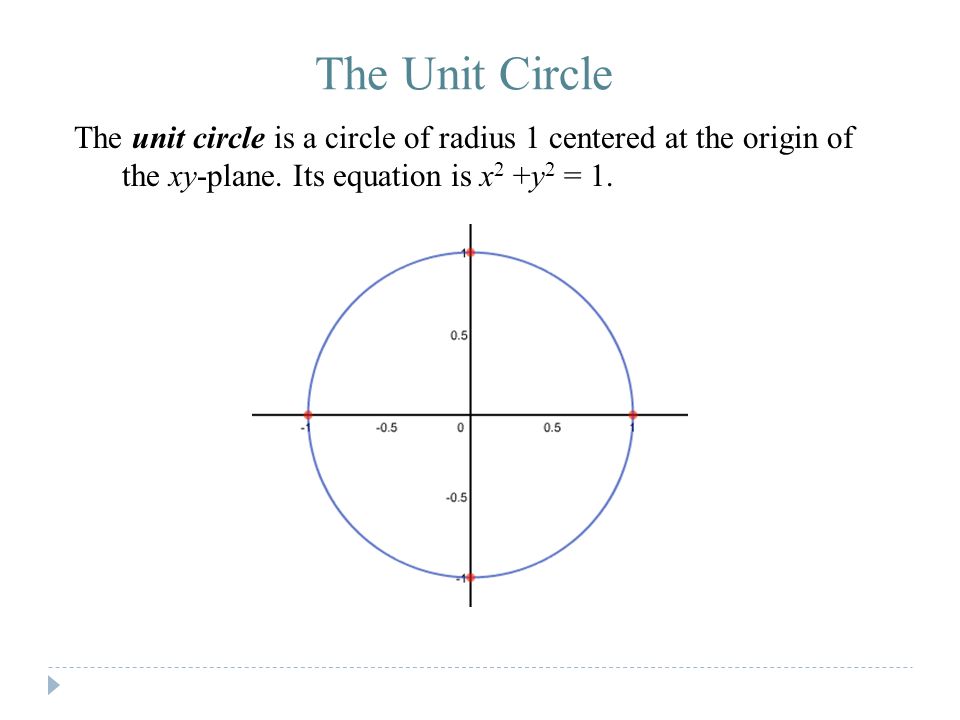
画像 x^2 y^2=1 circle 280200-X2 y2 1 circle
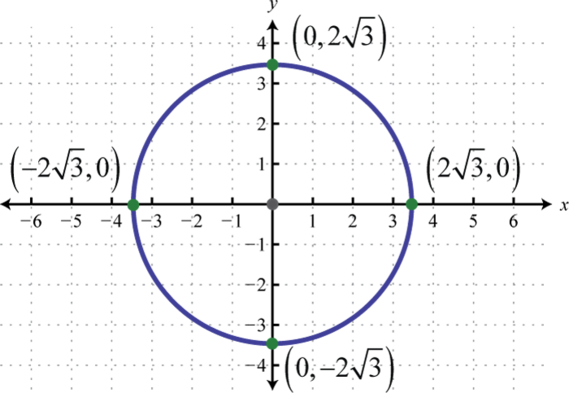
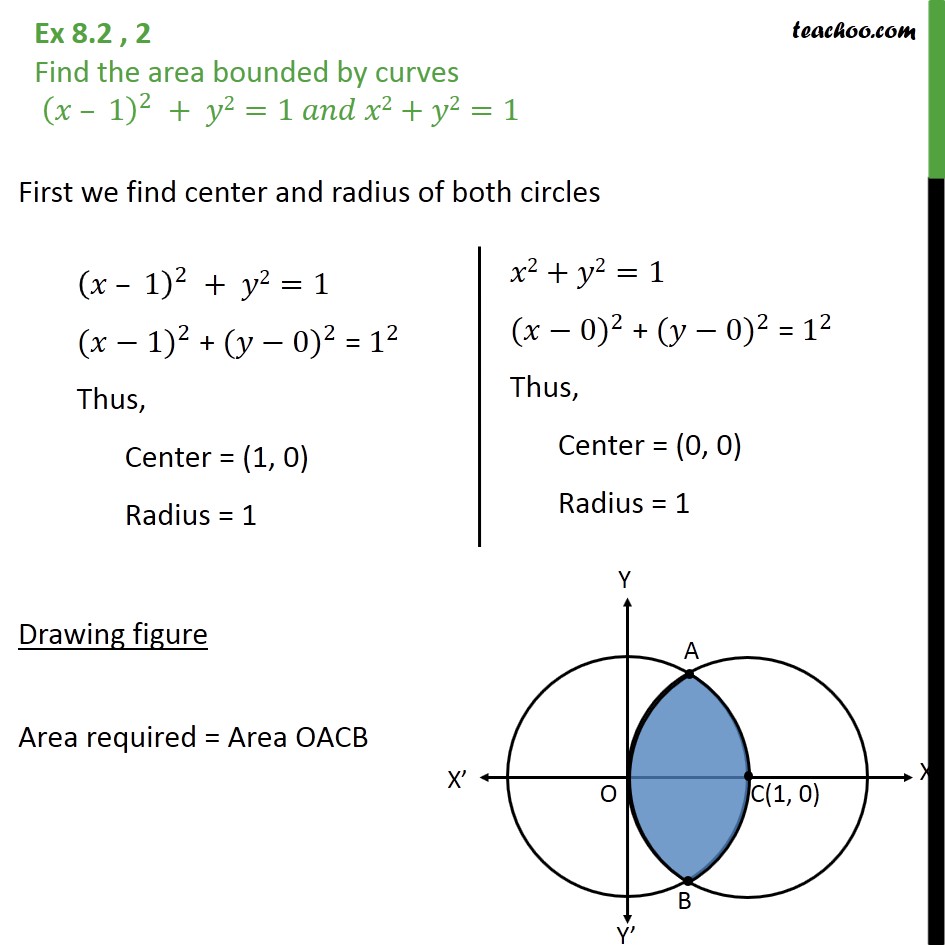
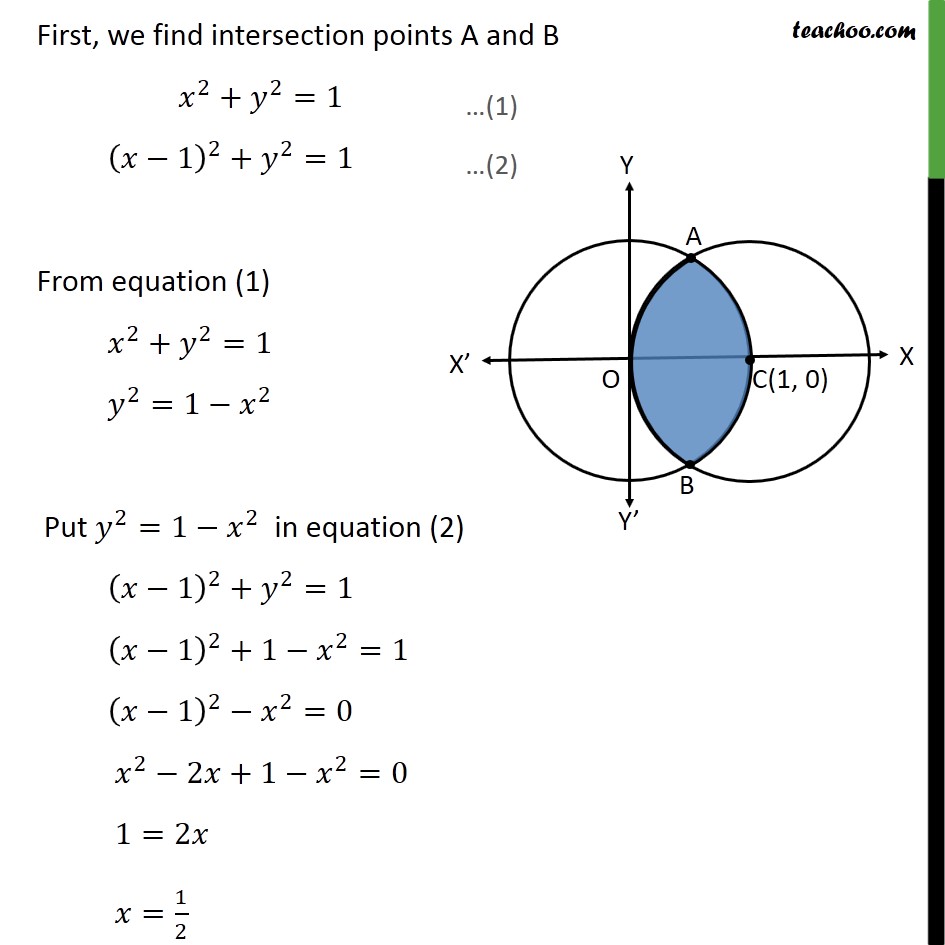
PROBLEM 2364 PEYAM RYAN TABRIZIAN Problem The gure shows a xed circle C 1 with equation (x 1)2y2 = 1 and a shrinking circle C 2 with radius r and center the origin P is the point (0;r), Q is the upper point of intersection of the two circles, and R is the point of intersection
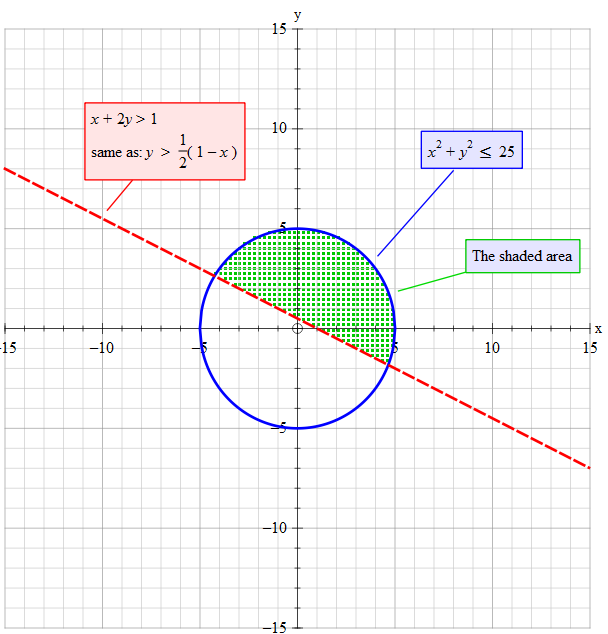
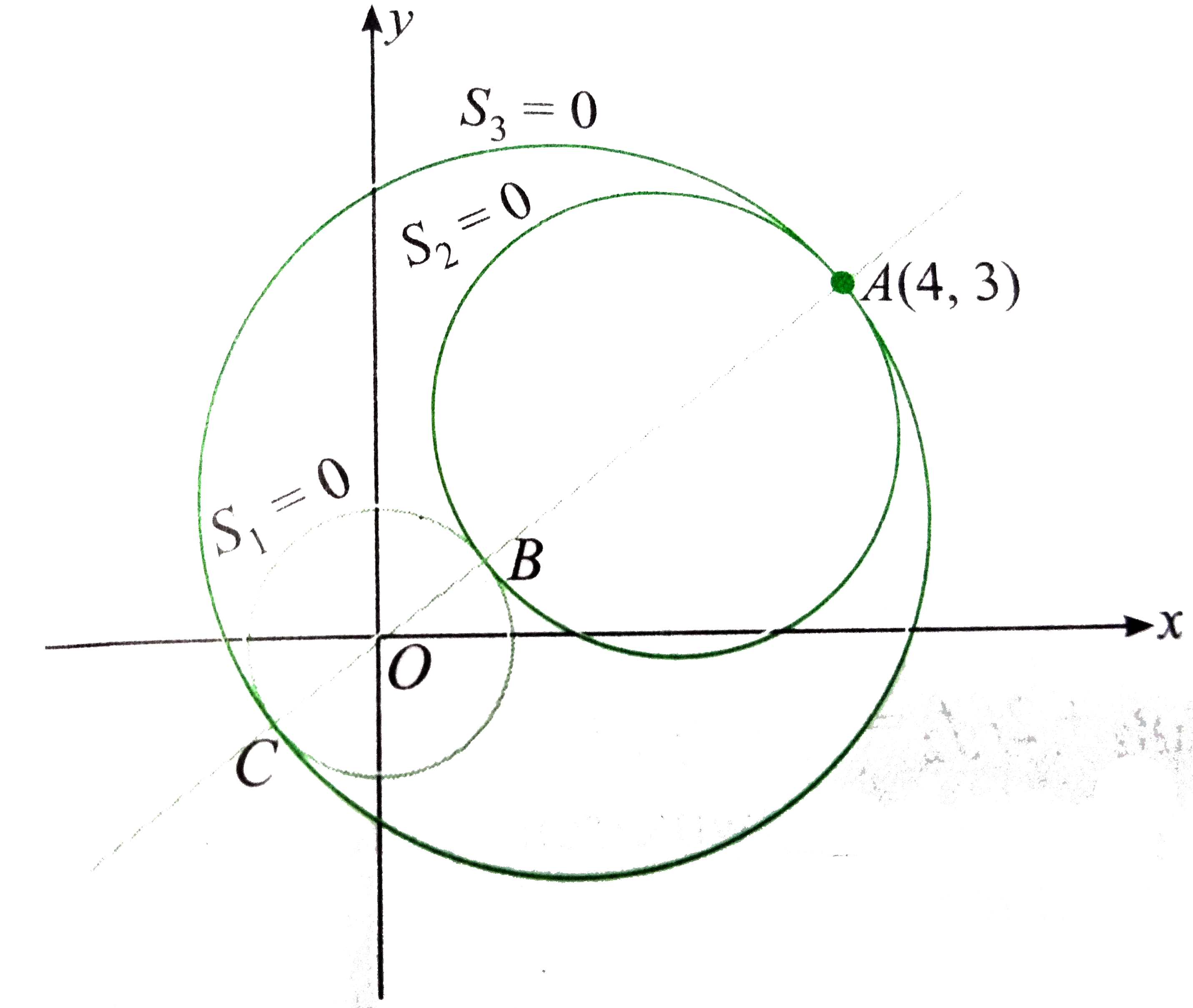
X2 y2 1 circle-Therefore the circle $$\{(x,y) \in \b R^2 x^2 y^2 = 1\} = f^{1}(\{1\})$$ is closed in $\b R^2$ Your set is also bounded, since, for example, it is contained within the ball of radius $2$ centered at the origin of $\b R^2$ (in the standard topology of $\b R^2$) Since $\{(x,y) \in \b R^2 x^2 y^2 = 1\}$ is a closed and boundedLemma 31 Let Cbe the circle with standard equation f(x,y) = x2 y2 2gx2fy c = 0 For every point P = (u,v), f(u,v) is the power of P with respect to the circle The radical axis of two circles is the locus of points with equal powers with respect to the two circles The radical axis of the two circles x2 y2 2g 1x2f1y c1 = 0, x 2y 2g
X2 y2 1 circleのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  |  |
 | ||
「X2 y2 1 circle」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「X2 y2 1 circle」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
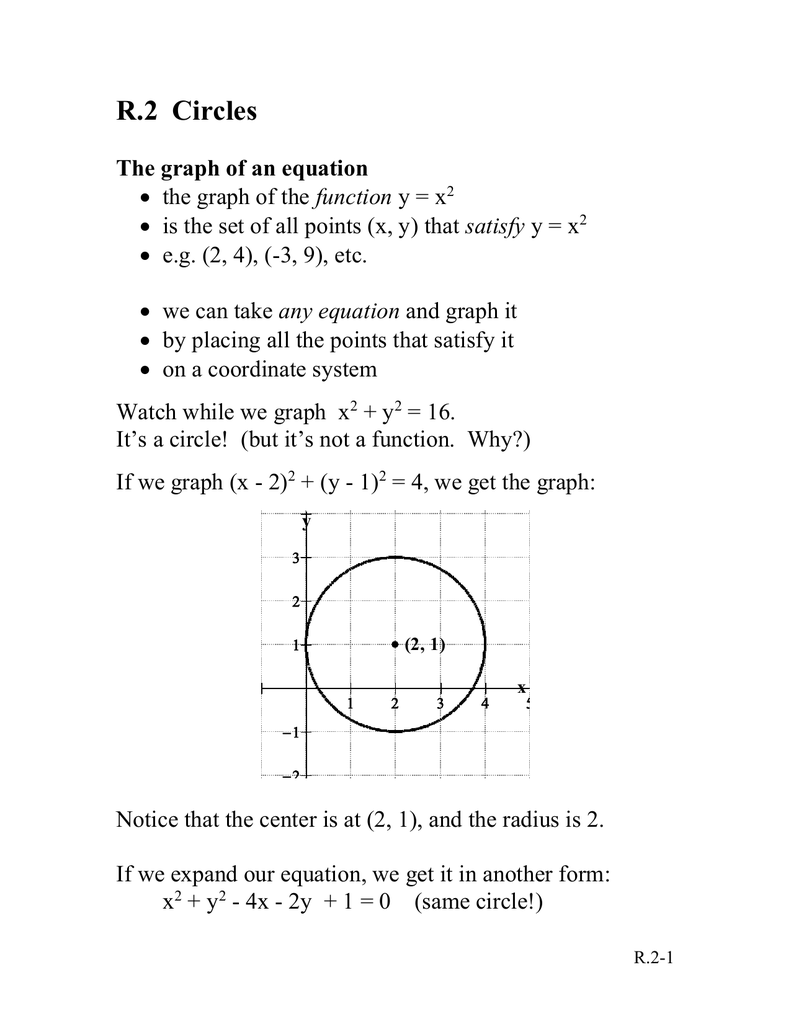 | 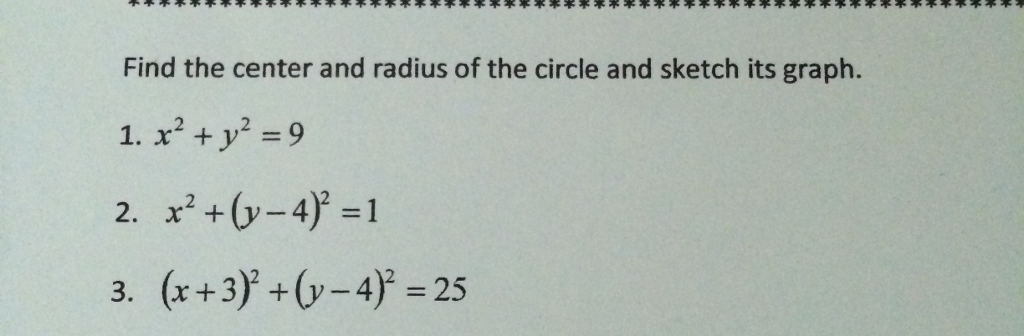 | |
 |  | 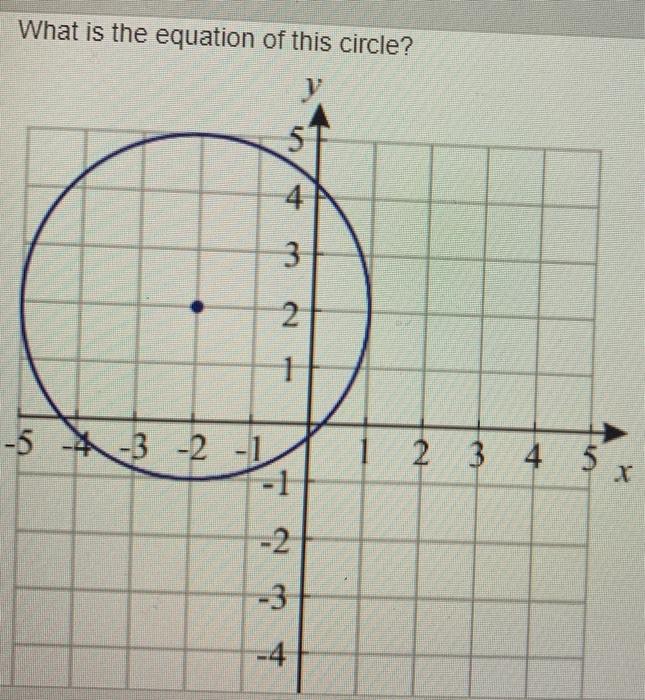 |
「X2 y2 1 circle」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「X2 y2 1 circle」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 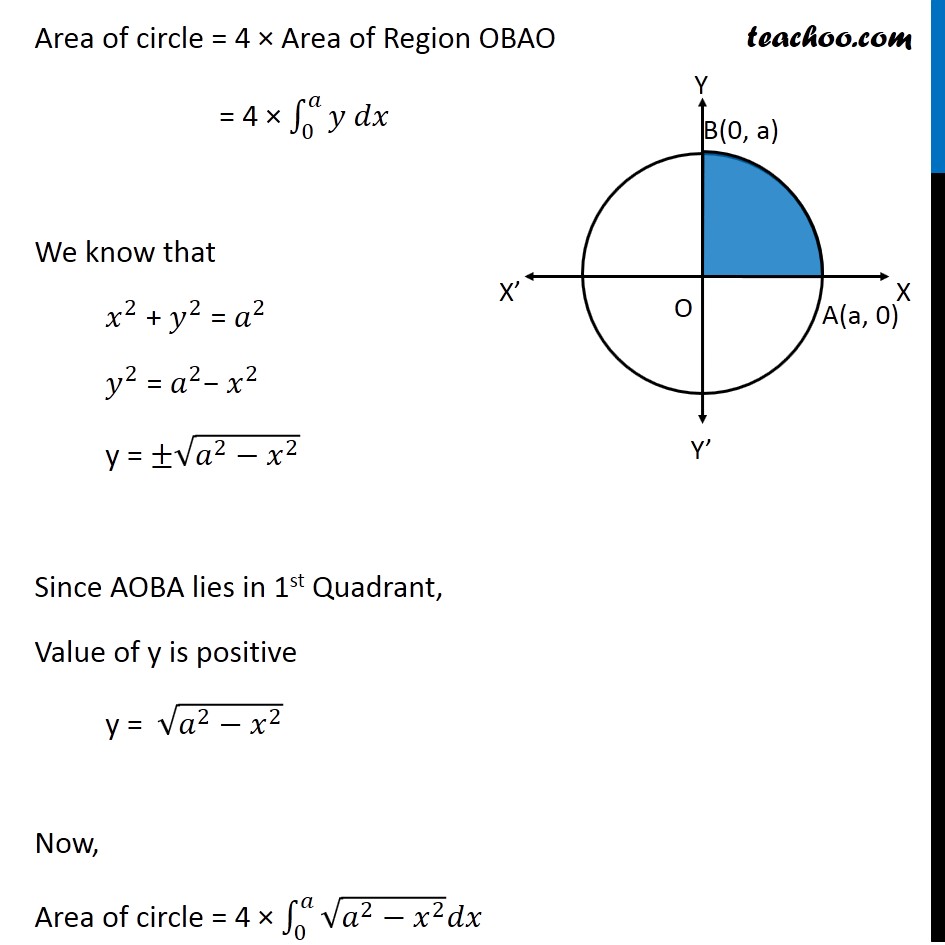 |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「X2 y2 1 circle」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「X2 y2 1 circle」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「X2 y2 1 circle」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 | ||
「X2 y2 1 circle」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  |
Y′ = xy(1−x2 −y2) Figure 2 shows how the associated velocity vector field looks on two circles On a circle of radius 2 centered at the origin, the vector field points inwards, while on a circle of radius 1/2, the vector field points outwards To prove this, we write the vector field along a circle of radius r as (3) x′ = (−yiY i (2) The co ordinates x and y in (2)are not arbitrary {they are related through equation (1) This means that w e are free to assign a v alue only one of the
Incoming Term: x2 y2 1 circle,
コメント
コメントを投稿